What is this IT field?

Definition
Software development encompasses a range of activities within computer science that focus on the creation, design, deployment, and support of software.The primary aim of this development process is to produce a product that effectively satisfies user requirements and aligns with business goals in a manner that is efficient, repeatable, and secure
Some essential components of this development process is Systems Analysis and Design, Programming and application development, and DevOps and System Development Life Cycle(SDLC) practice.
Systems Analysis and Design (SAD) is the discipline of studying how people, processes, and technology interact in organizations, and then creating or improving information systems to solve business problems.
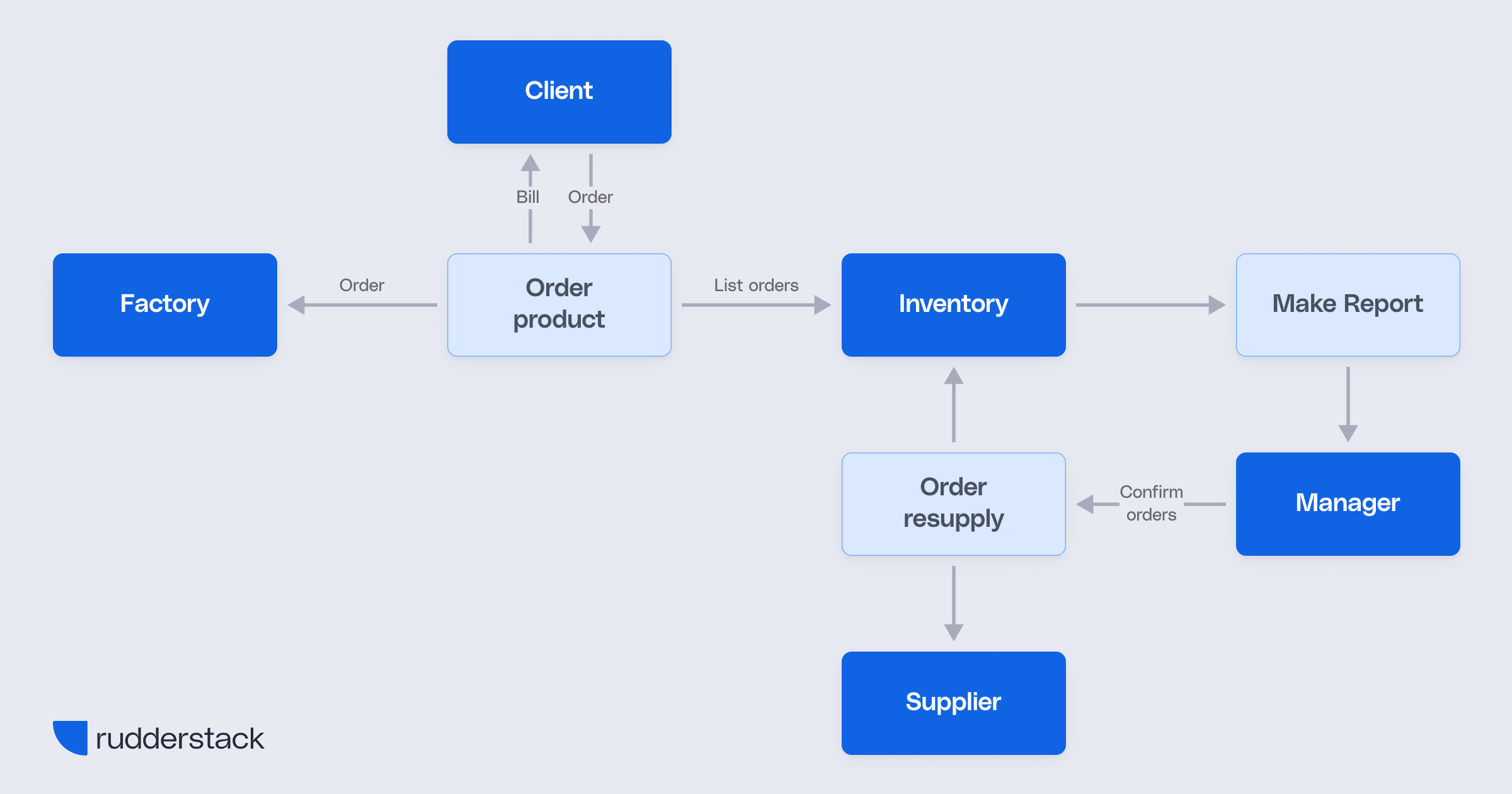
System design involves the process by which an organization may develop a newer system or strategy to complement or replace an existing system.
Programming and application development involves the design, creation, testing, and deployment of software.
DevOps is an approach to software development that involves cooperation between development and operations teams to more reliably and quickly deliver software.
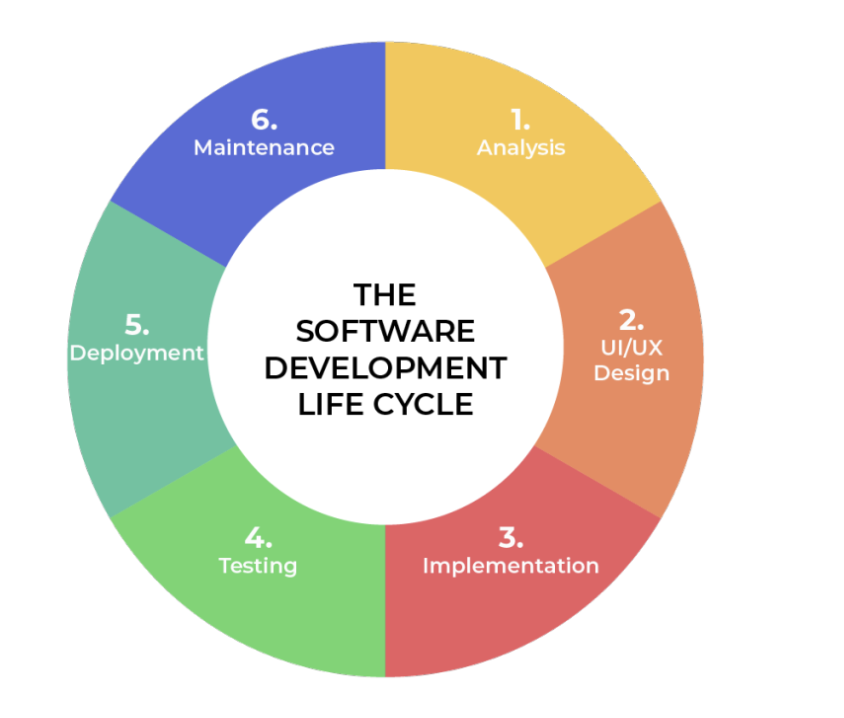
SDLC is a process that a software project follows from not only its start and finish, but also continued its maintenance.

Role in Organizations


- Acts as a bridge between business needs and technical solutions.
- Ensures systems align with organizational goals like efficiency, productivity, profitability, and growth.
- Reduces risks of failures by identifying issues early in the design process.
- Analyze potential vulnerabilities or threats to a system to implement preventative measures.
Typical Responsibilities & Daily Activities

- Gathering requirements through interviews, surveys, and observations.
- Analyzing workflows, data, and processes to identify inefficiencies.
- Designing system models (e.g., data flow diagrams, ERDs, UML diagrams).
- Collaborating with developers, project managers, and stakeholders.
- Testing prototypes and ensuring user acceptance.
- Oversee software programming.
Key Technologies & Tools



- Modeling and Diagramming tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, Draw.io help analysts create diagrams like data flow charts and UML diagrams, which show how systems work. They make it easier for analysts, developers, and stakeholders to share the same understanding of how processes and data connect.
- Databases are used to store, organize, and manage information that systems rely on. Developers and database administrators then build and maintain the database using platforms like MySQL, SQL Server, or MongoDB. These systems ensure data can be safely stored, retrieved, and updated as users interact with the application.
- Project Management tools like Microsoft Project, JIRA, Trello help teams plan, organize, and track work during system development. They make it easier to assign tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress. These tools keep everyone aligned and ensure the project stays on schedule.
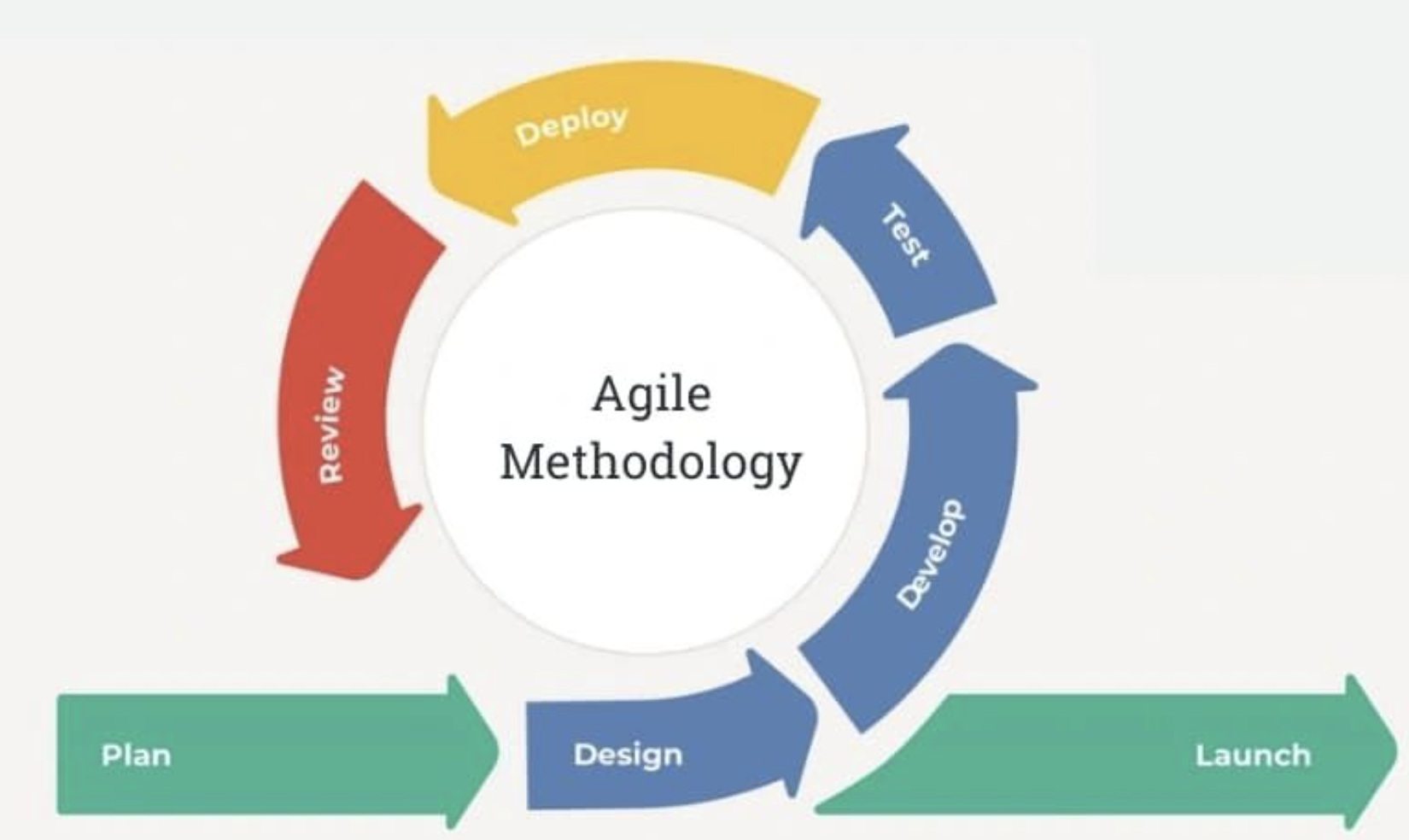
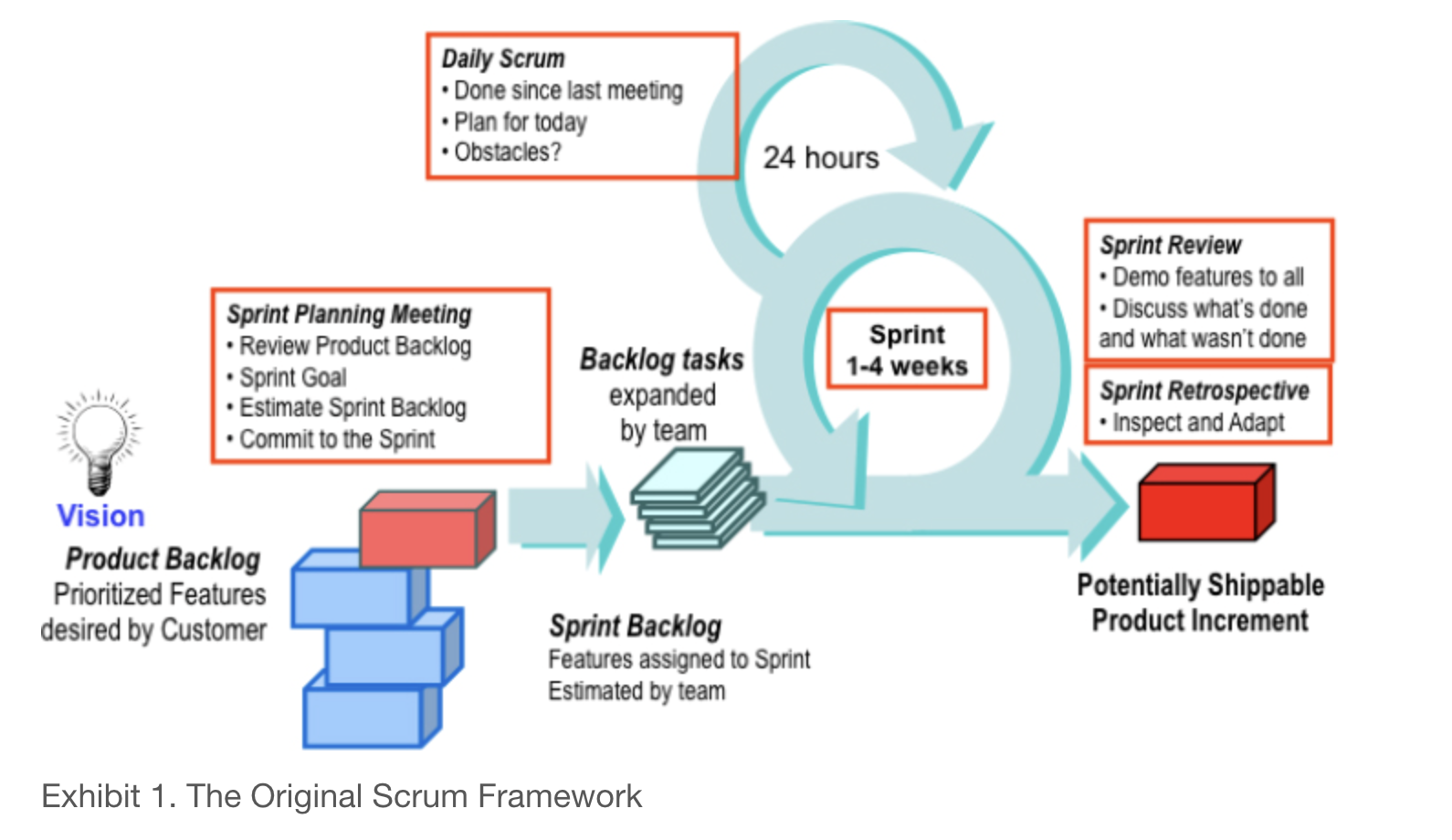
- Development Frameworks such as provide Agile, Scrum, SDLC models provide a structured approach to building systems where teams deliver small pieces, get feedback, and improve quickly. Analysts use these to translate user needs into tasks, clarify expectations, and ensure each stage delivers real value.